Strength training allows you to burn more calories, increase muscle mass and protect against the effects of aging by reducing your risk to diabetes, bone degeneration, and cardiovascular disease.

Weightlifting, strength training and bodybuilding are the same thing, aren’t they? They are to a certain degree but slight nuances produces different results. Bodybuilders don’t generally look like weightlifters.
Your body’s hormonal environment is in decline from the age of 30 onwards. Some research shows your metabolism starts to slow from the youthful age of 25. These 2 factors which increase your body fat and cause weight gain can be combated with strength training.
You may have read why strength training is vital for anyone over 40 throughout this site. This is the danger age when a lot of the effects of bad living can manifest as heart disease and diabetes.
You can use swimming for strength training and weight loss as the water provides natural resistance that is also very kind on the joints.

As you go past 50 and beyond it is vital to have strength in your muscles, tendons and joints if you want to have mobility and enjoy life to the full without restrictions brought about by sedentary living.
You don’t necessarily have to have been that inactive, just less proactive in building strength where it matters- and not just for the mirror!
If you are under 30 don’t go to sleep yet the lessons learned here will save you a ton of trouble in your future years.
There are more than just physical health benefits, resistance training makes you feel good. I can vouch for it being one of the best stress relievers there is. Great for clearing out your headspace.

What’s Good About Using Resistance Training To Increase Your Strength?
- Speeds up resting metabolism for up to 3 days after each exercise session
- burns fat
- increases lean muscle mass
- helps prevent insulin resistance
- lowers risk of diabetes
- improves circulation
- improves protein synthesis
- boosts testosterone and regulates hormones
- maintains joint strength and bone density
- reduces debilitating effects of ageing and slows down cellular ageing
- helps mobility
- good for depression & anxiety – boosts mood controlling neurotransmitters norepinephrine, serotonin, dopamine & GABA
- boosts neurotransmitter glutamate which is responsible for memory and learning
- weight training linked to reduced risk of alzheimer’s and memory loss
- prevents degenerative muscle loss conditions like sarcopenia
- intense strength training efficiently uses carbs (glycogen) and fat stores as fuel leading to less fat storage and better synthesis
- improves blood lip profiles – lowers bad cholesterol and triglycerides
- boosts protective HDL cholesterol
- improves heart function- remember the heart is the most important muscle!
Bodybuilding or Strength Building?
Bodybuilding increases muscle size (hypertrophy) by manipulating muscle cell and fiber physiology. Strength training focuses on the neuromuscular system. A good weight training routine applies the both. We have a full length discussion on the topic here.
We have discussed how a weakening grip can prematurely bring you to the end of life, and why it is not always breaking a hip that leads to death, but rather the decaying state of the muscles that support your skeletal structure.
If you don’t use it you lose it, definitely applies here. But with every dog and it’s owner talking about strength training- Facebook Walls, and Pinterest Boards bombard our smart screens every second of the day – but what actually is it?
Strength Training Definition
Strength training involves any type of resistance exercise that increases functional strength that carries over to everyday life, and not just in the gym. It can be done using free weights, bodyweight exercises, and even resistance bands.
It does not just mean wacking as much weight on a bar every week and seeing how much you can lift. It involves progressively overloading the muscles each week so that they increase in strength.
Bodybuilding favors higher reps and more working sets. At the extreme it can go as high as 10 sets with 15 reps. To optimally grow it’s advised to use between 40-60% of your 1 rep max. This combined with an excessive calorie surplus leads to a higher musculature (hypertrophy).
Strength training uses a lower rep range, 5-8 with a higher weight ratio – 80-90% of your 1 rep max. Set ranges can go between 1-5 usually.
A lot of strength training focuses on the core multi joint exercises that work more than one body part. Stability is essential to create the perfect environment for the strength to carry over to everyday life.
The core exercises are compound movements which involve more than one muscle group like the squat, bench press, push-up, military press, clean and jerk, barbell or dumbbell row. Exercises like bicep curls and triceps extensions are isolation exercises that focus on 1 specific muscle group.
Tricep pushdowns are an excellent isolation exercise for building the tricep muscles, which make up almost 75% of the upper arms. Don’t be the gym rat doing 300 bicep curls thinking you will build herculean arms. If you do this in the squat rack the bigger guys have the right to beat on you with macho insults.
The squat for example requires tremendous stability and coordination and involves the back, hamstrings, quadriceps, calves and buttocks and of course the core. It takes nearly every muscle in the body to correctly stabilize you to perform this exercise safely.
In real life terms this exercise carries over to increasing your body’s overall strength and can help protect your spine when lifting heavy objects in the correct manner. Simple things like sitting down and standing up if done incorrectly over time can damage the spine and your posture.
Many sportsmen and women incorporate strength routines with the goal of building stronger not larger bodies. This can be achieved by using the correct rep structure and consuming less calories.
Strength Training Essential For Boosting Hormones Responsible For Lean Muscle Mass
Simply put as you age testosterone, growth hormone and IGF-1 are on the decline usually at the age of 30 on, and sometimes even before it. These hormones are responsible for maintaining lean muscle mass and play an important part in ageing.
The same is true with the muscle paradigm, if you don’t use it you lose it. If you don’t tell the brain to keep producing these hormones by demanding your body to get stronger, the brain will slow down their production. The aging process will occur as your body has no need for strength.
Women face the menopause as they age and men the andropause which results in from the lowering of testosterone. Lower testosterone equals a decline in muscle production and a loss of sex drive.
As with the menopause the hormone fluctuations can severely impact mood, bone density, the metabolism and weight gain. The only way to naturally boost and regulate these hormones is via strength training, exercise and diet. Combining all 3 is the perfect antidote.
Go To The Gym With A Plan
If you go to the gym with a well orchestrated strength plan you will place a load on the body on a regular basis it has to cope with, and it will flood your body with these anabolic inducing hormones so it can come back bigger and stronger to deal with the force exerted on your muscles.
The offset of this is more lean muscle creation, fat stores burnt as fuel and stronger bones and tendons from the release of growth hormone.
Not only is this better for muscle building, but better for your health. Less fat equals less susceptibility to diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Weight training is essential for boosting GH, IGF-1 and testosterone. Without applying strength training these hormone levels decline faster than normal.
Fixing Work-Life Balance
Sitting all day at a computer as most of the world now does for hours on end a day can cause a strength loss and intrench bad posture habits which can strip our bodies of functional strength and overload our spines and necks as we sit in reinforced bad positions.

Sitting for long periods of time is not only bad for your bones, it can also be potentially fatal for your health. It slows down blood circulation, which is responsible for transporting nutrients around the body.
Chairs have been designed for aesthetics and comfort, sitting for most of the day robs your body of functional movement. This position actually damages the body. It causes the muscles to tighten, which brings its own mobility restrictions. Sitting with the spine hunched forwards compresses and damages the spine.
Sitting too long also causes fat to build up around the heart and other vital organs. Easy or comfortable living has its downsides. That’s why renowned mobility expert Kelly Starrett says “Sitting is death”.
One tip to deal with excessive sitting is to get up once every 30 minutes to break free from the shackles of a compromised position. Shake it all loose and then go back to the chair again. Lets face it, it can’t be avoided if that’s what your job requires.
Movement makes a difference, as does movement to and in the gym.
A tip to protect your spine during sitting is to tighten the abs just before you sit down. Trying to keep 10-20% of pressure in the abs protects your spine, and this endurance based exercise will also sculpt your abs.
Activate Those Genes!
Strength is not just for strength or showing off. It makes logical sense. As we are living self regulating organisms thanks to our inbuilt DNA, our bodies adapt to what they regularly are called to do. If you switch off exercise your genes will switch off your bodies response to it.
Your DNA sends out signals to its enzymes to synthesize more protein if the demand for strength increases in your body. The simplest way to do this is create a regular environment that requires something heavy to be moved.
Look at the benefits of a simple squat.
Doing squats in the correct form can build up leg and back strength which can help preserve the integrity of our joints, as the muscles do the jobs they were designed for, and we don’t actually rely on our joints to overdo what they are supposed to.
Strong muscles protect the integrity of our joints and take the stress off them.
It can also turbo charge your overall strength making you better able to cope with sports, lifting objects and the daily hustle and bustle of everyday life.
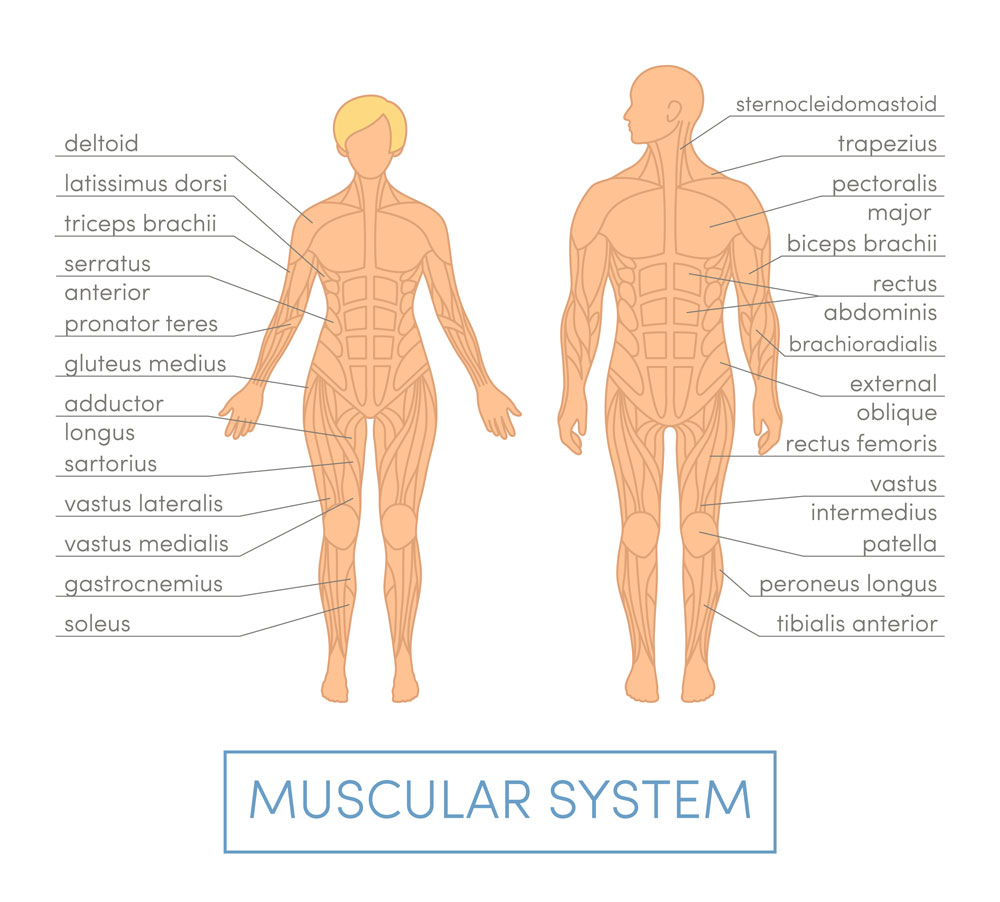
Muscle Loss Linked To Fat Storage
If your body is not actively producing muscle it is overactive in producing fat. Form the age of 30 onwards your body loses 3-8% of muscle mass per decade. Strength muscle mass, and muscle function is lost due to a condition known as Sarcopenia1.
To lessen the impact of this naturally occurring condition androgens, growth hormone, resistance training and insulin play major roles.
If you choose to neglect strength training completely you can lose 5 pounds of muscle per decade. That may not seem all that bad but the body has a major accomplice which also plays a vicious role in changing your body structure and health.
Resting metabolic rate or RMR decline up to 3% per decade2 after the age of 30. This age is the key factor for hormone deceleration. A slower metabolism lends to weight gain.
Lack of muscle and fat gain increases your bodyfat percentage. High levels of fat in your body mass index (BMI) increases the risk of cancer, diabetes, joint pain and cardiovascular disease.
Some research suggest muscle burns 9 calories per hours, untrained individuals burn 6 calories per hour in their resting metabolic state (RMR). Whilst others disagree on this exact amount, what isn’t in question is it takes the body a lot of energy to create and maintain muscle mass.
MUSCLE IS ONE OF THE LARGEST FACTORS THAT DETERMINES YOUR RESTING METABOLIC RATE AS IT IS METABOLICALLY ACTIVE. IT RESPONDS TO STIMULUS OR LACK OF.
With decreased muscle and a slowing metabolism it’s easy to add 15-20 pounds of fat per decade. Nature has it’s way of showing the whole world this with enlarged waists and sagging, puffy skin.
Weight gain and loss of muscle mass is a lethal toxin. One compounds the other. They are perfect foes in the degeneration of your body.
But science has made us wise to both and a perfect solution is offered. It just requires a bit of work.
One of the factors in your control over your metabolism is your activity level. You can keep your RMR going at a higher level with resistance training.
Bone Density Benefits
Strength training has been proven to maintain bone health7 by maintaining bone thickness and preventing osteoporosis and sarcopenia (skeletal muscle loss) which is key to being fit and active in later years. Bone mass starts to decrease as you age, a simple fall in your youth can be lights out in your 70’s.
The fundamental component behind strength training is functional strength. As the majority of these exercises involves stabilizing the pelvis and working from a solid base this strength carries over into the real world, producing stronger hips, backs, legs and shoulders, and of course better balance.
Whats the pain of a few squats compared to the pain and loss of mobility due to a hip replacement?
Once you are putting a demand on your body to keep strong it has no other option but to make your muscles stronger and activate those bone cells to keep producing strong bones and tendons.
Research backs this up as Mosti et al., 2014, discovered a 12 week squat program8 caused spinal bone mineral density to increase up to 2.2%.
Exercise & Insulin
Insulin levels are drastically impacted if you take exercise out of your lifestyle. The body can become resistant to insulin if you don’t exercise as you get older.
Insulin shuttles amino acids into muscle as part of protein synthesis, without it the body is very inefficient at producing muscle.
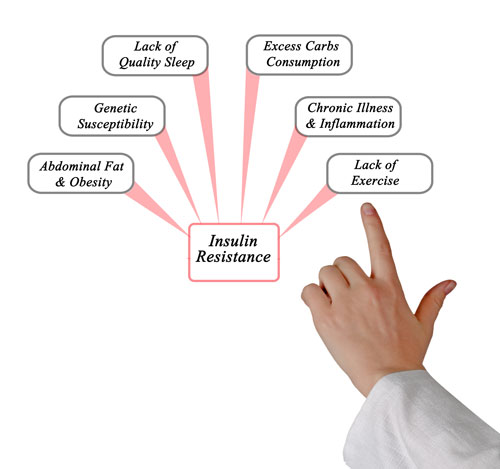
When the body becomes resistant to insulin it can’t use if effectively – this adds to the loss of lean muscle mass as the uptake of glucose into muscle tissue declines and is instead manifested as excessive sugar levels in the bloodstream.
Sadly this insulin resistance is not brought on by genetic factors, but lifestyle choices. Lack of exercise can be the main precursor as bodyfat levels take over as muscle degenerates.
As muscle tissue becomes insulin resistant less amino acids (essential for protein synthesis) are taken up by cells. An effect called anabolic resistance occurs.
A drop in insulin levels lowers circulation and this results in muscle degeneration, and thus the downward spiral continues. We can learn a lot from professional bodybuilding lingo as anabolism equals growth.
Staying as anabolic as you can helps you build and maintain muscle mass.
Loss of muscle and strength is not the only thing to deal when insulin resistance occurs. Type 2 diabetes 3 is linked to muscle loss and disability for aging individuals who have very little muscle mass.
A lot of the problems of Western world seems to stem from having too much but doing too little. Type 2 diabetes is preventable for most people, and if you do not take care of your body your risk of acquiring it goes through the roof.
Diet, weight control and exercise are key.
Rejuvenating The Anabolic Environment
To set your body up for the best health and muscle/body fat balance, anabolic resistance needs to be counteracted. You best friend here is to turn the body into a state of anabolism. The best way forward is with resistance training.
Remember anabolic resistance is attributed to poor circulation. Applying resistance with weight training several times per week can reset your muscle and strength balance, increase your circulation, enhance protein synthesis by delivering more amino acids to muscle cells, and increased glucose uptake into you muscles.
What is key for fat burning is that exercise increases your metabolism. High intensity strength training and aerobic exercise4 increases your metabolism especially as you age. This type of short, intense exercise is preferred to long, slow, ambling workouts that lack intensity and energy.
The result is less body fat, more muscle mass, more strength and better health. One key anabolic proponent that ensures all this occurs as your body is forced into making more muscle mass, is it uses fat to burn as fuel.
As glycogen is transported into muscle tissue for days after each workout as part of the repair process, your resting metabolic rate rises to aid with the process. Muscles require more energy to function than fat.
The EPOC (Afterburn effect) kicks in after you leave the gym. The resting metabolic rate rises as your body consumes more oxygen as repleted muscle tissues and organs need replenishment.
Check how much calories your metabloism uses each day
How Often Do You Need To Train?
If the training requirements sounds like too much, research shows that a few short exercise sessions per week can make all the difference. You need to get up and move. Sitting for instance lowers blood pressure which can lead to cardiovascular disease.
2-3 weight training routines a week of 30-45 minutes can counteract the stress, work and posture conditions that have been imposed on the body.
Harvard Medical School and numerous research studies confirm that 20 minutes of strength training 3 times a week is enough to build strength. To main motivation and keep your body in an anabolic state, workouts should not go higher than 45 minutes.
20 minutes of intense work in the gym is way more productive than 90 minutes of slow paced drudgery. Research shows slow paced cardio sessions are bad for your health. Cheap treadmills are all the rage, but using them incorrectly can be bad for your health.
If you are short on time, or just don’t cardio, a better workout solution is to combine a low impact machine like the Bowflex Max Trainer. Easy on the joints and 14 minutes or less can get the job done.
Build Your Home Gym
Build a home gym costs less than you might think. If you add up your gym subscription you can soon save on the price of a home gym in 2 years. The beauty is that you have the freedom to train when you like, take charge of the musice, the atmosphere and the clientele.
Plus you can wear whatever you like. Have a look at out our home gym reviews. Start with the unique plate free Blaze which uses resistance rods, and then try the EXM 3000 if you prefer heavy iron.
If you do not have a lot of space, but want a wide variety of weights have a look at these bowflex dumbbells. They replace 30 sets of dumbbells and they save a heck of a lot of space, and do away with lining up loads of dumbbells on the floor or paying for a dumbbell rack.
Keep Strong Well Into Your Senior Age
Strength training has no age cap. Most people lose half their strength from the ages of 30-90. This study done on people in their 90s5 shows nonagenarians were still able to increase their strength and accumulate muscle mass well into their 90’s.
That’s one way to maintain independence. A fall from someone at this age can be treacherous. Creating strength creates stability. Stability helps maintain balance. It also makes you more resistance to illnesses and more able to cope with sickness.
Frailty shortens many seniors life span exponentially. Being frail is also linked to Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive decline6.
If you have taken years off training the good news is that you can rebuild muscle tissue again even if you are between the ages of 50-90+, as the research above clearly shows. There is hope for everyone. So no one has an excuse to slack!
Campbell et al. & Patley et al. 1994 showed a 3-4 pound muscle increase in an over 50 studies after 12-16 weeks of strength training. It’s remarkable what the body can do if you put your back into it.
Contrast that to 30% of the U.S. population suffering from sarcopenia which is a loss of skeletal muscle mass so severe it effects every day tasks such as having the strength to be able to walk freely, or to even being able to get up out of a chair.
Doing Cardio The Old Way?
Cardio has certainly changed in the last 15-20 years. It used to be you would do 30 mins on the exercise bike, 30 minutes on the treadmill, or go outdoors for a run. Then ellipticals and exercise bikes came in to soften the impact of running and using the treadmill.
The only problem is people are staying way too long on these machines at an ambling pace. Slow to mid paced cardio has it’s place, but just not 3 times per week.
As exercise bikes like the Pooboo are so cheap it’s easy to get caught in an endless loop of slow to medium paced cycles which can actually be ok to pass the time, but produce minimal results.
Long cardio kills your gains and decimates muscle mass. Short bursts of powerful cardio sessions can be performed safely on the Assault fan bike or Airdyne pro stationary bike. These bikes are way tougher than traditional spin bikes, but research has shown they burn more calories in a shorter timespan which compliments your strength and muscles gains.
If you are not a fan of the treadmill rowing can also compliment your strength sessions, and keep your heart in great shape.
Have a look around this site as there are many workouts for men and women over 40 that involve strength, cardio, HIIT & circuits. HIIT is short for High Intensity Interval Training – it stops you killing your muscle gains due to the brevity of the workout.
If you want a complete program that has broken down all the steps you need to take 40 Strong will certainly speed up your results.

- 1 Muscle Tissue Changes With Aging Sarcopenia Study Elena Volpi, Reza Nazemi, and Satoshi Fujita
- 2 Aging, basal metabolic rate, and nutrition Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi.
- 3 Effects of insulin resistance on skeletal muscle growth and exercise capacity in type 2 diabetic mouse models Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab
- 4 Strength training increases resting metabolic rate and norepinephrine levels in healthy 50- to 65-yr-old men J Appl Physiol (1985). 1994 Jan;76(1):133-7
- 5 Multicomponent exercises including muscle power training enhance muscle mass, power output, and functional outcomes in institutionalized frail nonagenarians Eduardo L. Cadore, Alvaro Casas-Herrero, Fabricio Zambom-Ferraresi, Fernando Idoate, Nora Millor, Marisol Gómez, Leocadio Rodriguez-Mañas, Mikel Izquierdo
- 6 Frailty is associated with incident Alzheimer’s disease and cognitive decline in the elderly Buchman AS1, Boyle PA, Wilson RS, Tang Y, Bennett DA
- 7 The Effects of Progressive Resistance Training on Bone Density M E Nelson J E Layne
- 8 Maximal Strength Training Improves Bone Mineral Density and Neuromuscular Performance in Young Adult Women Mats P Mosti, Trude Carlsen, Elisabeth Aas, Jan Hoff, Astrid K Stunes, Unni Syversen
